Hints
A hint is an instruction passed to the optimizer through comments in an SQL statement. Hints enable you to make decisions normally made automatically by the optimizer.
In a test or development environment, hints are useful for testing the performance of a specific access path. For Example, you may know that a specific index is more selective for specific queries. In this case you may use hints to instruct the optimizer to use a better execution plan, as in the following example.
select  /*+  index (s, sales_prd_idx) */ order_id, sales_date, amount, name  from sales_history s where customer_id=1000
The INDEX hint uses the table alias and the index on that table. Other types of hints . Sometimes hints can get ignored see here why?

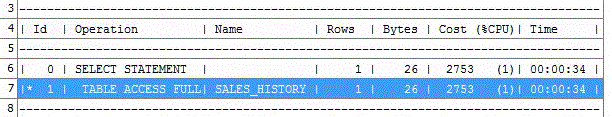
Clearly its doing a full table scan and not doing an index scan. To force an index scan we add a hint in the second query.

This example is to purely demonstrate the function of hints and how it can be used (Not an example of how hints can be used to improve performance)
Forcing a Joining Method
select s.sales_date, s.order_id, s.product_id, p.product_name, p.standard_cost, p.color, p.list_price, p.product_size, p.weight, p.product_category from sales_history s, product p where s.product_ID= p.product_id and s.Product_ID=101 /* This one uses the nested loop join */ /* but if we find it to be sub optimal we can change the join type by using Hints such as merge Join or hash Join */ select /*+ USE_MERGE(S) */ s.sales_date, s.order_id, s.product_id, p.product_name, p.standard_cost,p.color, p.list_price, p.product_size, p.weight, p.product_category from sales_history s, product p where s.product_ID= p.product_id and s.Product_ID=101 select /*+ USE_HASH(S) */ s.sales_date, s.order_id, s.product_id, p.product_name, p.standard_cost, p.color, p.list_price, p.product_size, p.weight, p.product_category from sales_history s, product p where s.product_ID= p.product_id and s.Product_ID=101



The optimizer does not always make the best decision in determining the correct path (or join method) for executing an SQL. This is were Hints can be used to determine what would be the best execution path.
For all your application development needs, visit www.verbat.com for a fiscally conscious proposal that meets your needs ( So I can keep this blog going as well!!!!)
Alternatively click through the link if you found this article interesting. (This will help elevate my companies Search engine rankings)

Leave a comment